Designing a digital product is a difficult task that requires being not only UX expert, but you also need to understand the areas for which you create the product, the needs of the audience that will use it, etc. Product development involves many people, the process forces everyone to work closely with each other, including designers, developers, product owners, strategists, founders, and most importantly, users.
So, how to correctly organize this complex process of product design?
This article is going to be rather short, but straight to the point guide, as here we are going to talk about key steps of the product design process and actionable methods product designers use during each stage. Let’s dive in!
Product design stages
Before we proceed to our main topic, we’d like to emphasize that though we are going to talk about steps (something that goes one after another) of product design this process is not linear. To create a usable and appealing product that meets client needs and company goals, the design team has to constantly move backward and forward from step to step to test and refine the product.
Now let’s start discussing the process itself.
Conducting research
The research phase aims at defining the problem the team will work on during the design process.
Collecting data provides valuable information that allows you to draw conclusions about the prospects of the project. It is necessary to conduct research, even if there is clear confidence in the positive outcome. Many products turn out to be useless to people, and companies lose profits. Analyzing the preferences of the target audience and determining the problems that people can solve with the help of the product helps to avoid such problems.
At the research stage, you need to collect all the data that affects the use of the project.
Let’s see what methods you can use to effectively pass this stage:
User interview

Image credit: ferpection.com
Conducting interviews is a simple and straightforward method of researching your potential clients, learning their opinions, motivation, feelings, or the way they use some products.
To conduct a high-quality and useful user interview, you should prepare a list of questions and make the person feel comfortable talking about the product and its goals. Asking additional questions and clarifying will help you find the essence – what clients expect to receive with the product. It will help to understand the needs and characteristics of customer behavior, define new directions that are promising and interesting for clients.
Competitive analysis

Image credit: henkinschultz.com
The main goal of a competitive analysis is to obtain information about the advantages and disadvantages of your rivals, learn more about their strategy for the development of the product.
Strong points of your competitors will show in which direction to move, while weak points can help you understand how to create a better solution.
Moodboard
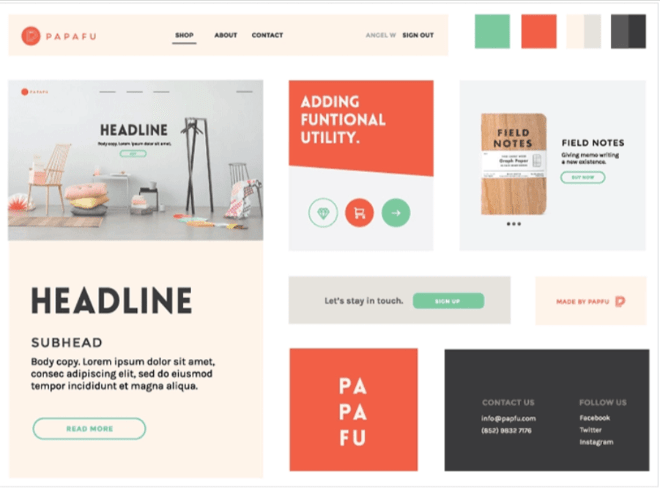
Image credit: justinmind.com
Moodboard is a collection of visuals and references that represent the style of your project. With the help of a moodboard, you can show clients or stakeholders an approximate look of the project without spending much time or money.
There are tons of sites for inspiration – Dribble, Behance, Pttrns, Pinterest, etc. and there you can easily find projects similar to yours. In addition, it is even possible to find some solutions to the problems you work on.
Developing strategy
UX strategy is a detailed plan of how the design of a future app will look and work. At this stage, the product team generates ideas, validates and visualizes them.
Here are the most effective methods of the strategy stage:
Brainstorm

Image credit: segalbenz.com
Brainstorming, as one of the methods of strategy stage, involves team members from different departments gathering together to generate and validate a set of ideas for a design solution before choosing the optimal one.
Customer journey map

Image credit: blog.hubspot.com
A customer journey map is a table or infographic that shows all the points of contact of a consumer with a product from the moment of the first interaction.
This map displays the client’s actions, thoughts, emotions, and problems they face and serves as a tool that helps improve the customer experience.
User flow
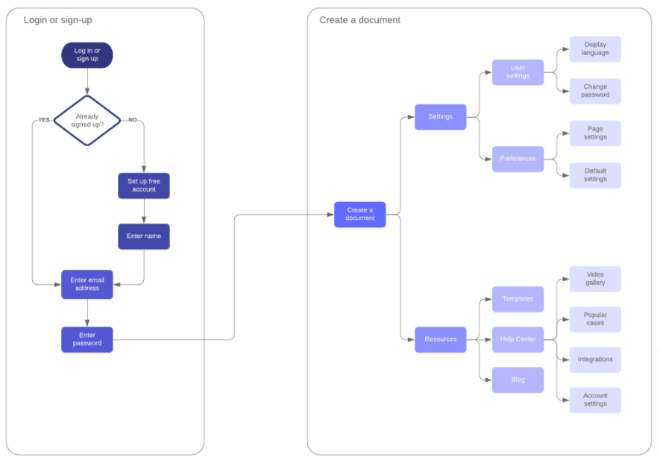
Image credit: medium.com
User flow represents the steps user takes when interacting with the product. It looks like a diagram that shows the path of a user to their goal. Building user flows help to understand at what point the customer may have troubles and how designers can improve them.
Wireframes
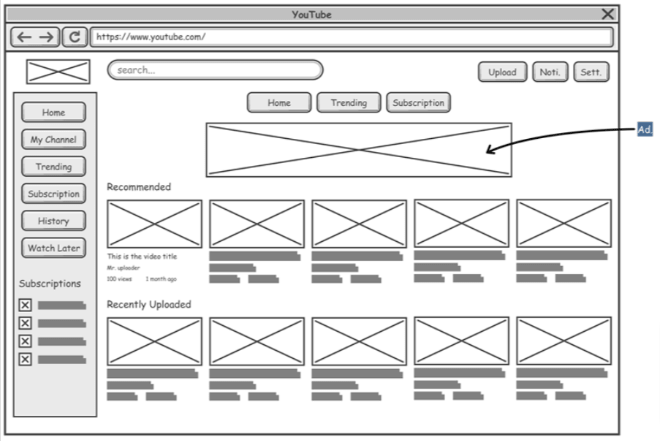
Image credit: archimetric.com
Wireframe presents the structure of the page. It shows the location of design elements on each page and how they connect with each other. They serve as a visual guide for designers on how to build the product.
Designing a prototype
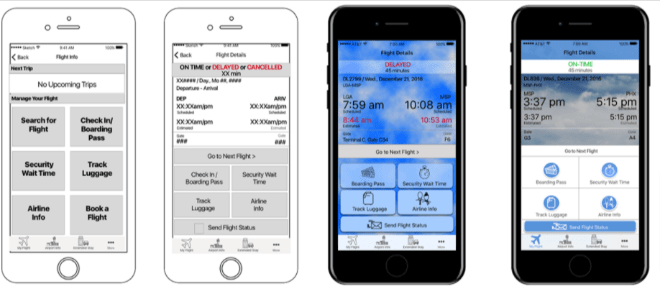
Image credit: pinterest.com
Prototyping is a very important piece of the design puzzle. It helps to convey the vision of the product to customers and illustrates the desired result to the developers.
A prototype is a basic structure of the product with main elements and features. It is like a simulation of the complete product and very often it has a clickable layout. The main function of the prototype is to quickly test the idea with minimal cost. Usually, product designers create prototypes in Figma, Adobe XD, Invision, or Framer.
Testing
You may perform different types of testing. The main objective of this stage is to come to the final conclusion that there are no bugs in the product and it is ready for release.
Usability testing

Image credit: usabilitygeek.com
Usability testing involves a user performing certain actions with the prototype (or product) and you collect their feedback and see how prospects cope with different tasks, where they have troubles or misunderstandings.
A/B testing

Image credit: searchbusinessanalytics.techtarget.com
A/B testing means that you give different versions of your product to different users and collect feedback. Then you have to compare the results to understand which version is more successful.
The product is never complete, it is always evolving
Going through a cyclical process of data analysis, feedback from users, and testing you will always know what is your next step. As new issues emerge, there will be the need to add new features to the product. The methods listed above will help you work through these challenges correctly, with more confidence and understanding.
It was a short overview of the topic, in case you need more information read the complete guide on product design.




